
All proteins are made from combinations of the 20 amino acids show below. Proteins are another class of enormously diverse organic molecules that are made from multiple units of simpler molecules arranged in chains. Enzymes also attach to the ribosomal complex and aid in the process of translation, in which the coded sequence of bases on the mRNA is translated and directs the synthesis of a chain of amino acids, which are the building blocks of proteins. Once the mRNA emerges from the nucleus, it attaches to a two part structure called a ribosome, which consists of ribosomal RNA (rRNA). The mRNA then leaves the nucleus through special pores in the membrane of the nucleus. Transcription takes place inside the cell nucleus where chromosomal DNA is located. Transcription is the process by which a gene, segment of DNA that encodes for a specific protein, serves as a template for the synthesis of a messenger RNA (mRNA) for that specific protein. This short animation from the Discovery Channel provides a nice overview of the transcription and translation.

An Overview of Transcription and Translation For the time being the video below provides an overview of this process that will be helpful. This process will be clearer when we explore it in more detail in another online module. This newly synthesized messenger RNA will then leave the cell nucleus and move to the cytoplasm of the cell where the RNA will in turn be used as a template to synthesize a specific protein. In a highly regulated process, cellular enzymes can unwind a particular segment (gene), and other enzymes move along a gene using one strand of DNA as a template to synthesize a complementary strand of messenger RNA. A single chromosome contains thousands of genes, segments of DNA that encode for specific proteins. In essence, each chromosome is a gigantic molecule of double stranded DNA wound tightly into a double helix.
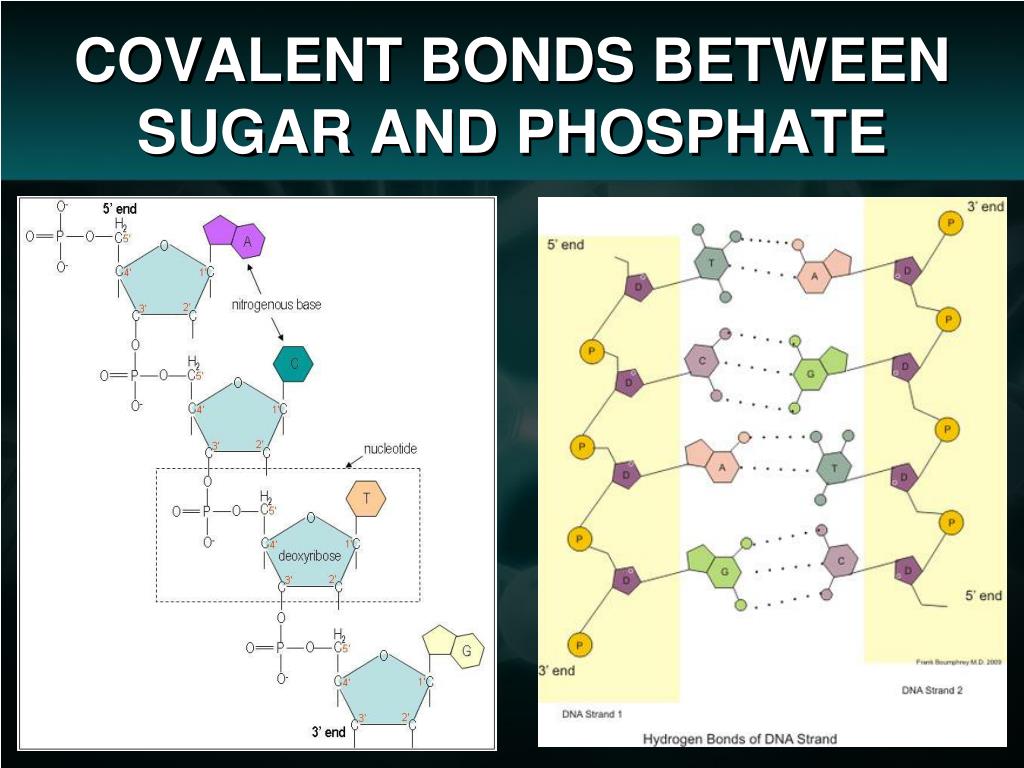
Dna sugar phosphate backbone covalent bond code#
The cells of living organisms have chromosomes which contain an inherited code for synthesizing all of the proteins that the organism produces.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
